Knee pain is a common problem that can affect people of all ages. The knee is a complex joint that plays a crucial role in our daily activities such as walking, running, and climbing stairs. When the knee is injured or becomes weakened, it can lead to pain, discomfort, and difficulty with movement. In this blog post, we will explore the function of the knee, common symptoms of knee pain, potential causes, and treatment options, including exercises and physiotherapy. We will also discuss when it is appropriate to seek physiotherapy consultation for knee pain.
Knee Function
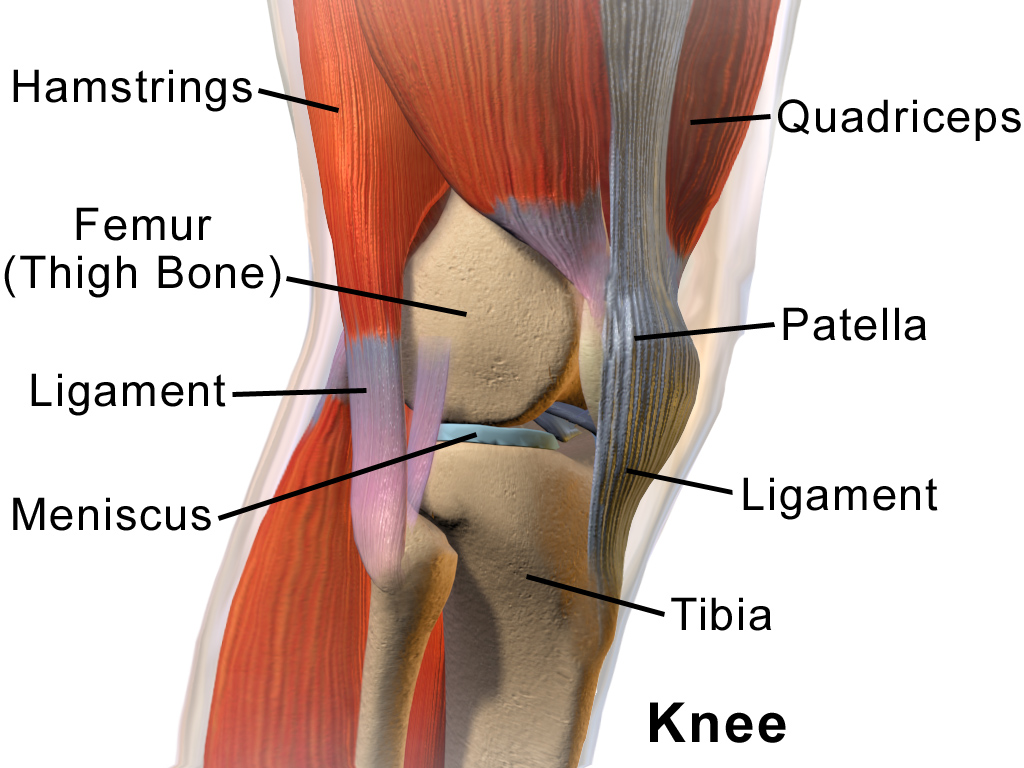
The knee is a hinge joint that connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shinbone (tibia). Several ligaments and tendons support it, including the ACL (anterior cruciate ligament), PCL (posterior cruciate ligament), MCL (medial collateral ligament), and LCL (lateral collateral ligament). These structures provide stability and support to the knee joint. The knee also contains a layer of cartilage called the meniscus, which acts as a shock absorber and helps to distribute weight evenly across the joint.
Symptoms and Causes of knee pain
It can manifest in a variety of ways, including:
- Aching or throbbing pain in the knee
- Stiffness or difficulty moving the knee
- Swelling or redness around the knee
- Popping or grinding sounds when moving the knee
- Weakness or instability in the knee
- Sometimes, knee pain can refer or cause pain to other areas of body including lower back, hip, ankle/foot and vice versa.
The severity of these symptoms can vary, and they may come and go or be constant. Potential causes are:
- Arthritis: This is a common cause of knee pain, particularly in older adults. Arthritis is a degenerative condition that can cause inflammation and damage to the joint, leading to pain and stiffness.
- Injuries: Knee injuries such as sprains, strains, and fractures can all cause pain. These injuries can be sports related or can occur because of accidents, falls, or overexertion.
- Overuse: Repetitive strain on the knee, such as from running or jumping, can lead to overuse injuries such as patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS), runner’s knee or shin splints.
- Structural abnormalities: Certain conditions, such as malalignment of the knee or abnormalities in the shape of the bones, can cause knee pain.
Treatment Options for Knee Pain
There are several treatment options, including:
- Rest: Taking a break from activities that cause pain can help reduce inflammation and allow the knee to heal.
- Ice: Applying ice to the knee can help reduce swelling and numb the area to reduce pain.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help reduce inflammation and ease pain.
- Physiotherapy: A physiotherapist can develop a treatment plan that may include exercises to strengthen and stabilize the knee, as well as techniques such as massage and joint mobilization to reduce pain and improve function.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair, replace or reconstruct damaged structures in the knee.
Exercises for Knee Pain
Depending on the cause and severity, a physiotherapist may recommend certain exercises to help reduce pain and improve function. These may include:
- Quadriceps strengthening exercises: Strong quadriceps muscles can help stabilize the knee and reduce pain. Examples of quadriceps strengthening exercises include leg presses and squats.
- Hamstring strengthening exercises: Strong hamstrings can help support the knee joint and reduce the risk of injury. Examples of hamstring strengthening exercises include leg curls and glute bridges.
- Balance and proprioception exercises: Improving balance and proprioception (the ability to sense the position and movement of the body) can help reduce the risk of falls and further injury to the knee. Examples of balance and proprioception exercises include single leg stands and balance board exercises.
- Core strengthening: Improving dynamic control on one leg is important if you’re in sports or wish to improve performance. Example of core strengthening includes donkey kicks and bird dog with pelvis in neutral position.
Guidance on When to Seek Online Physiotherapy
If you are experiencing persistent or severe pain, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a physiotherapist. A physiotherapist can assess your condition and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan.
Online physiotherapy can be a convenient and effective option for those who cannot visit a physiotherapy clinic in person due to distance, mobility issues, or busy schedule. Online physiotherapy typically involves virtual sessions with a physiotherapist through video conferencing, during which the physiotherapist can assess your condition, provide guidance on exercises and other self-care techniques, and answer questions you may have.
When done properly; exercises decrease pain, improves movement, and build muscle and bone strength. I have treated many of my patients across BC with knee pain and helped watched them recover fully. This is something KB Physio offers as part of our online physiotherapy services. If you would like to get virtual physio treatment, without travelling or waiting at a clinic, and/or to get started quickly; get in touch with us (778) 658-6949 or email us.
Further readings
- Benefits of Physical Therapy after total knee replacement. https://medhab.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/Effects-of-Virtual-Exercise-Rehabilitation-In-Home.pdf
- Exercise and Osteoarthritis https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/j.1469-7580.2008.01013.x
- Noncontact ACL injuries and prevention strategies https://journals.lww.com/jaaos/fulltext/2000/05000/noncontact_anterior_cruciate_ligament_injuries_.1.aspx